SQL Server: Everything about SQL Server
Database Mirroring step by step and all Question and Answer of SQL Server
Database mirroring.
Friends believe me it’s very easy and anybody can create the mirroring and
work on it.
For testing I am creating mirroring
on using single computer.
We need following stuff to
configure mirroring in SQL Server 2008:-
1 . Principle
Server – It’s the server where our main
primary database available.
2 . Mirror
Server – It’s the server where we have
to transfer the data.
3 . Witness Server – It’s the server which responsible for automatic FAILOVER.
4 . Service
account- We can use default SA account credential for this
5 . SQL Agent- It should be running mode on both instance.
For above 3 server means need 3
instance of SQL server. In my case these are the server name-
1. Principle Server Name- JAIMATADI
2. Mirror Server Name – JAIMATADI\MSSQLSERVER_2
3. Witness Server Name- its optional server. Show
that I am not using witness server. It this case data loss may be happen. So for
best practice we should use witness server.
Step1:- Connect to Principle Server JAIMATADI and Mirror Server JAIMATADI\MSSQLSERVER_2 with service
account(In our case we are using SA account)
Please see below-
Step2:- Now we have to take 2
backup Full and transactional on principle server(JAIMATADI) to restore on
Mirror server(JAIMATADI\MSSQLSERVER_2).
To
take the backup we can you below query or wizard option.
1 1.
Full backup-
Using below query we can take the full backup-
BACKUP DATABASE [MirroringDB] TO DISK = N'E:\MirroringDB_Full_Backup.bak' WITH NOFORMAT, NOINIT, NAME = N'MirroringDB-Full Database
Backup', SKIP, NOREWIND, NOUNLOAD, STATS = 10
GO
declare @backupSetId as int
select @backupSetId = position from msdb..backupset where database_name=N'MirroringDB' and
backup_set_id=(select
max(backup_set_id) from msdb..backupset where
database_name=N'MirroringDB'
)
if @backupSetId is null
begin raiserror(N'Verify failed. Backup
information for database ''MirroringDB'' not found.', 16, 1) end
RESTORE VERIFYONLY FROM DISK = N'E:\MirroringDB_Full_Backup.bak'
WITH FILE = @backupSetId, NOUNLOAD, NOREWIND
GO
OR
You can use
below simple step:-
Rigth click
on database -->Task --> Baclup --> Add --> choose the location ('E:\MirroringDB_Full_Backup.bak') and
backup type: select FULL
2 2.
Transactional backup- Using below query we
can take the Tlog backup
BACKUP LOG [MirroringDB] TO DISK = N'E:\MirroringDB_Tlog_backup.Bak' WITH NOFORMAT, NOINIT, NAME = N'MirroringDB-Transaction
Log Backup', SKIP, NOREWIND, NOUNLOAD, STATS = 10
GO
declare @backupSetId as int
select @backupSetId = position from msdb..backupset where database_name=N'MirroringDB' and
backup_set_id=(select
max(backup_set_id) from msdb..backupset where
database_name=N'MirroringDB'
)
if @backupSetId is null
begin raiserror(N'Verify failed. Backup
information for database ''MirroringDB'' not found.', 16, 1) end
RESTORE VERIFYONLY FROM DISK = N'E:\MirroringDB_Tlog_backup.Bak'
WITH FILE = @backupSetId, NOUNLOAD, NOREWIND
GO
OR
You can use
below simple step:-
Rigth click
on database --> Task --> Backup --> Add --> choose the location ('E:\MirroringDB_Full_Backup.bak') and
backup type: select as Transactional log
Step3:- Using step2 now we have
backup file. Now we will restore the backup
on Mirror server. To restore we can use below query or wizard option. See below-
1 1 Restoring Full backup with NORECOVERY option
RESTORE DATABASE [MirroringDB] FROM DISK = N'E:\MirroringDB_Full_Backup.bak' WITH FILE = 1, NORECOVERY, NOUNLOAD, STATS = 10
GO
OR
You can use
below simple step:-
Right click on database in object
explorer --> restore database.. -->
In General Tab -->give name of DB To database: MirroringDB -->
Select file from device option (N'E:\MirroringDB_Full_Backup.bak') --> Go to options
Tab in Same wizard and select NO RECOVERY option.
2
2 2 Resotoring
transactional log backup with NORECOVERY option
RESTORE LOG [MirroringDB] FROM DISK = N'E:\MirroringDB_Tlog_backup.Bak' WITH FILE = 1, NORECOVERY, NOUNLOAD, STATS = 10
GO
OR
You can use
below simple step:-
Right click on database in object
explorer --> restore database.. -->
In General Tab --> give name of DB To database: MirroringDB -->
Select file from device option (N'E:\MirroringDB_Tlog_backup.Bak) --> Go to options
Tab in Same wizard and select NO RECOVERY option.
Step 4:- Now refresh the
both SQL Server instance. We will get
same database in both server(principle and mirror server) see below-
Step 5:- Now we can start the
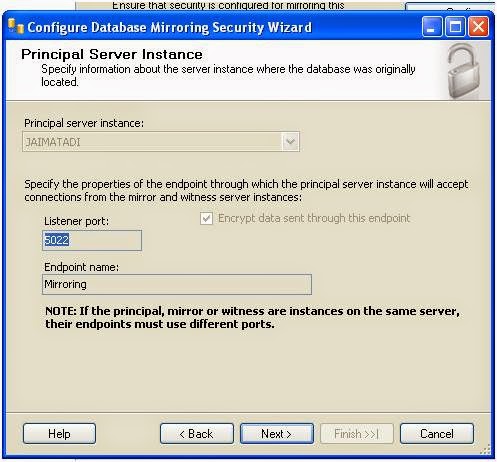
mirroring configuration- Please follow below simple steps and see screen shot.
Right click on MirroingDB database on
principle server --> Task --> Mirror --> click on Configure Security button. We will
get below screen and click next --> click
on No radio button --> Next -->
select Mirror server in drop down and Click on Connect button --> Login into mirror server --> Next --> Next --> Finish --> Close -->
Click on Start Mirroing button -->
Click on Yes -->Now
you can see the Mirror is done --> Refresh both SQL server instance and see the
MirroringDB database.
Step 6:- Using Failover option
you can change the mirroring. See below option.
Open database properties on
primciple server --> click on Mirroring tab --> click
on Failover button --> Click Yes --> refresh the
SQL Server Instance and see the change.
We can also change the Operation mode High Safety mode
(Synchronous) to High performance mode
(Asynchronous)
We can also Pause the mirroring using
Pause button.
All Question and Answer of SQL Server Database
Mirroring
1)
What is Database
Mirroring? What are the benefits of that?
Database mirroring is an option to improve the
availability of a databases which supports automatic failover with no loss of
data. This is new feature in 2005.
Benefits:-
a)
Increases data protection
b) Increases
availability of a database
c)
Improves the availability of the production database during
upgrades
2)
What are the
prerequisites for Database Mirroring?
a)
Both Servers are requires same edition either Standard
Edition or Enterprise Edition.
b)
If Witness server configured, the server should be
installed Standard Edition, Enterprise Edition, Workgroup Edition, or Express
Edition.
c)
All Servers should use the same master code page and
collation.
d)
Mirror Server has same database name and use only With
NoRecovery option.
e)
Mirroring uses the full recovery model. (Simple and
bulk-logged not supported)
f)
All logins for connecting Principal Database should be
reside on Mirror database
3)
What are the
Restrictions for Database Mirroring?
a) Maximum 10
databases per instance can support on a 32-bit system.
b) Database
mirroring is not supported with either cross-database transactions or
distributed transactions.
4)
Explain about
Principal, Mirror and Witness Servers?
1) Principal Server:- One Server serves the
database to client is called Principal server and it having original data. Can
have only one Principal Server and it has to be on a separate server.
2) Mirror Server:- Other server instance acts as a hot or warm standby server is called
Mirror server and it having copy of database.
3) Witness Server:- The witness server is an optional server and it controls automatic
failover to the mirror if the principal becomes unavailable. To support
automatic failover, a database mirroring session must be configured in
high-availability.
5)
In which
Operations are running the Operating Modes?
Asynchronous:-
Under asynchronous operation, the Principal server does not wait for a response
from the mirror server after sending the log buffer.
Synchronous:- Under synchronous operation, the Principal server sends
the log buffer to the mirror server, and then waits for a response from the
mirror server.
6)
What are the
Operating Modes and explain them?
a.
High
Availability:- High-availability
mode, runs synchronously. Requires a Witness Server instance. The
Principal server sends the log buffer to the mirror server, and then waits for
a response from the mirror server.
b.
High
Protection:- High-protection mode,
runs synchronously. Always commit changes at both the Principal and Mirror.
c.
High
Performance:- High-performance
mode, runs asynchronously and the transaction safety set to off. The
Principal server does not wait for a response from the mirror server after
sending the log buffer. The principal server running nice and fast, but could
lose data on the mirror server.
7)
What is End
Point? How u create end point?
An endpoint is a
network protocol which is used to communicate Principal, Mirror and Witness
servers over the network.
Creation of an end point:-
Create endpoint
<endpoint name> State=started/stopped/disabled
as tcp (listener
port=5022/5023) for database_mirroring (role=partner/witness)
8)
What is the
default of end points (port numbers) of principal, mirror and witness servers?
How to find the Port numbers?
The default port
numbers of principal, mirror and Witness servers are 5022, 5023 and 5024.
To
Find Port Number:- SELECT name, port FROM sys.tcp_endpoints
9)
Which Trace flag
is used in Mirroring?
Trace flags are
used to temporarily set specific server characteristics or to switch off/on a
particular behavior. 1400 Trace flag is used in mirroring.
To set trace flag for Database mirroring:- Configuration
Manager > Right click on server instance > Properties > Advanced tab
> Startup parameters > -t1400 (add)
10)In which Recovery
model we can use in Mirroring?
In mirroring the
principal and mirror databases are used only full recovery model
11)What is Role-switching?
Inter changing of
roles like principal and mirror are called role switching.
12)What is the
syntax to stop the Database Mirroring?
T_SQL:- Alter database <database name> set partner off
GUI:- SSMS:- > Click on Principal database > Task > Mirror > Remove
mirroring
13) How to failover
the mirror database manually?
T_SQL:- Alter database <database name> SET PARTNER FAILOVER (Do on principal database)
GUI:- SSMS:- > Click on Principal database > Task > Mirror > Failover
14)How to configure
Mirroring?
a)
Choose Principal Server, Mirror Server, and optional Witness server.
b)
The principal and mirror server instances must be running
the same edition either Standard Edition or Enterprise Edition
c)
The Witness server instance can run on SQL Server Standard
Edition, Enterprise Edition, Workgroup Edition, or Express Edition
d) Mirror
database requires restoring a recent backup and one or more T.log backups of
the principal database (with Norecovery)
15)How to monitoring
Mirroring?
There are six
methods are available for monitoring the Database Mirroring
a)
Database
Mirroring Monitor:- Database Mirroring Monitor is a GUI tool
that shows update status and to configure warning thresholds.
To open DM Monitor:- Right click on Principal Database > Tasks > Select Launch
Database Mirroring Monitor.
b) SQL Server Management Studio:- A green arrow on the mirror server is indicates
running well. A red arrow indicates problems that need to investigate.
c)
SQL Server Log:- It provides
information of Mirroring establishment and status. If any errors occurs it will
be logged to SQL Server log and Windows event log.
d) Performance Monitor:- It can provides real-time information about Database mirroring. We
can use performance counters to get status of the database mirroring such as
Bytes received/sec, Bytes sent/sec, Transaction delay etc.
e)
Profiler:- Profiler many
events are providing the status of the Database mirroring
f)
System Stored
Procedures:-
·
sp_dbmmonitoraddmonitoring
·
sp_dbmmonitorchangemonitoring
·
sp_dbmmonitorhelpmonitoring
·
sp_dbmmonitordropmonitoring
16)What is
Hardening?
As quickly as
possible, the log buffer is written to the transaction log on disk, a process
called hardening.
17)What is Log
buffer?
A log buffer is a
special location in memory (RAM). SQL Server stores the changes in the
database’s log buffer.
18)How to Set a
Witness Server to Database Mirroring?
SSMS:- Right Click on
Principal Database > Tasks > Mirror > Click on Configure Security >
Provide the End point for Witness server > Click oK
T-SQL:- ALTER DATABASE AdventureWorks SET
WITNESS = 'TCP://prasad.local:5024' (Do this from the Principal Server)
19)How to Remove a
Witness Server from Database Mirroring?
SSMS:- Right Click on
Principal Database > Tasks > Mirror > Remove TCP address from the
Witness > Click oK
T-SQL:- ALTER DATABASE AdventureWorks SET
WITNESS OFF
20)How to Setup
Fully Qualified Names for Database Mirroring?
I.
FQDN Error
One or more of the server network addresses lacks a fully qualified
domain name (FQDN). Specify the FQDN for
each server, and click Start Mirroring again.
The syntax for a fully-qualified TCP address is:
TCP://<computer_name>.<domain_segment>[.<domain_segment>]:<port>
II. RECTIFYING FULLY QUALIFYED NAMES
v To View Endpoints:-SELECT * FROM sys.database_mirroring_endpoints;
v Remove existing all Endpoints from Principal,
Mirror and Witness servers :- DROP ENDPOINT
[ENDPOINT_NAME]
v Adding "local" as the primary DNS suffix
as follows:-
1)
Right-click My Computer, and then click Properties.
The System Properties dialog box will appear.
2)
Click the Computer Name tab.
3)
Click Change. The Computer Name Changes dialog box will
appear.
4)
Click More. The DNS Suffix and NetBIOS Computer Name dialog
box will appear.
5)
Enter the appropriate DNS suffix for the domain.
6)
Enable “Change primary DNS suffix when domain membership changes”
check box.
7)
Click OK to save the changes, and then click OK
to exit the Computer Name Changes dialog box.
8) Click OK
to close the System Properties dialog box, and then restart the
computer for the change to take effect.
v Reconfigure the Database mirroring either GUI or T-SQL
21)What are the
Database Mirroring states?
1) SYNCHRONIZING:-
The contents of the mirror database
are lagging behind the contents of the principal database. The principal server
is sending log records to the mirror server, which is applying the changes to
the mirror database to roll it forward.
At the start of a database mirroring
session, the database is in the SYNCHRONIZING state. The principal server is
serving the database, and the mirror is trying to catch up.
2) SYNCHRONIZED:-
When the mirror server becomes
sufficiently caught up to the principal server, the mirroring state changes to
SYNCHRONIZED. The database remains in this state as long as the principal
server continues to send changes to the mirror server and the mirror server
continues to apply changes to the mirror database.
If transaction safety is set to FULL,
automatic failover and manual failover are both supported in the SYNCHRONIZED
state, there is no data loss after a failover.
If transaction safety is off, some
data loss is always possible, even in the SYNCHRONIZED state.
3) SUSPENDED:-
The mirror copy of the database is not
available. The principal database is running without sending any logs to the
mirror server, a condition known as running exposed. This is the state
after a failover.
A
session can also become SUSPENDED as a result of redo errors or if the
administrator pauses the session
SUSPENDED
is a persistent state that survives partner shutdowns and startups.
4) PENDING_FAILOVER:-
This
state is found only on the principal server after a failover has begun, but the
server has not transitioned into the mirror role.
When
the failover is initiated, the principal database goes into the
PENDING_FAILOVER state, quickly terminates any user connections, and takes over
the mirror role soon thereafter.
5) DISCONNECTED:-
The
partner has lost communication with the other partner